Scoliosis Treatment
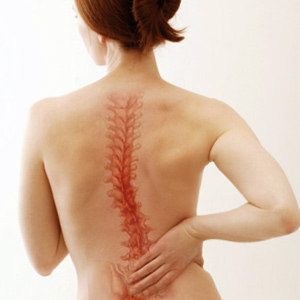
Scoliosis is a descriptive term derived from the Greek word 'skoliosis' meaning 'crooked condition.' Scoliosis is a physical deformity in which the spine of the individual looks more like an 'S' or 'C' than a straight line. Normally due to scoliosis, the spinal column curves 10 degree or less.
While all spines have curves in the neck, upper trunk or lower trunk, scoliosis occurs when there are abnormal side to side lateral curves in the spine column. It is a three dimensional complex deformity which can be clearly viewed on an x-ray from the rear.
Scoliosis affects roughly 2% of women and 0.5% of men in the general population. This medical condition is common in girls during late childhood.
Types of Scoliosis
Scoliosis can be congenital, idiopathic or neuromuscular. The several types of scoliosis are named and
defined according to the cause, age and the nature of spinal curvature. Scoliosis, is broadly classified under two heads namely, structural and non structural.
While structural scoliosis is caused by:
- neuromuscular diseases
- certain infections
- birth defects
- injury and connective tissue disorders
- metabolic diseases
- rheumatic disorders
- tumors
Non structural or functional scoliosis can be due to certain underlying conditions:
- such as difference in leg length,
- spasms in muscles, and
- Inflammatory conditions like appendicitis.
Idiopathic scoliosis
Although over 80% of scoliosis cases are idiopathic, due to no known cause, it could be largely genetic. A
medical breakthrough in this direction by researchers at Texas Scottish Rite Hospital for Children in May 2007 identified the first gene associated with idiopathic scoliosis CHD7. Idiopathic scoliosis as such can be broadly classified under four categories:
- Infantile, in children aged 3 and under
- Juvenile, in children 3-9 years of age
- Adolescent, from 10 -18 years of age and
- Adult, after skeletal maturity occurs.
In approximately 80% of the cases, adolescent idiopathic scoliosis occurs at the onset of puberty.
Congenital scoliosis
This is a rare type of scoliosis which is caused due to failure of formation or segmentation of the spine. This type is mostly detected among females. It exists at the time of birth due to congenital vertebral anomaly and occasionally it could be due to an underlying anomaly such as tethered spinal cord. Lateral spinal curves develop during infancy due to congenital scoliosis. Absence of vertebrae, partially formed
vertebrae and failure of the vertebrae to form normally are some of the reasons for this condition.
Thoracic scoliosis
This is so categorized on the basis of the spinal curvature. Neuromuscular scoliosis of this category is formed due to muscular weakness or neuromuscular disease such as cerebral palsy, spina bifida, paralytic conditions and tumors and muscular dystrophy. In adults due to the age factors one can detect degenerative scoliosis, with the weakening of the spinal cord.
In the thoracic or thoraco-lumbar region scoliosis, the mechanics of the curve are such that the rotation of the vertebrae occurs in combination with lateral curvature. This produces a protuberance of one side of the rib cage. This is seen well when the person leans forward.
Whereas, in the case of congenital scoliosis, vertebral anomalies are present even at the time of birth, in idiopathic condition the cause is unknown but most seen in infantile, juvenile adolescent or adult. In neuromuscular instances of scoliosis, the condition has developed as a secondary symptom after a physical trauma. Significantly, this condition seems to affect around 7 million in the US.
Mild scoliosis
Mild scoliosis implies that it is not serious and the curvature is less than 20 degrees. This condition generally does not require any treatment (unlike severe scoliosis which warrants treatment), other than monitoring.
Mild scoliosis is seen to occur in up to 50 % of the population, where a scoliosis is a lateral or sideways curve in the spine which is quite apparent while viewing the spine from the rear.
Scoliosis, as such, is not rare as it affects one in every ten person and many among them have mild scoliosis, while some are not even aware of it.
Spine scoliosis
The spine in the human body is made up of several individual bones called vertebrae; joined together by muscles and ligaments. Each of the vertebrae is cushioned by flat and soft discs that separate one from the other. As such the spine is flexible and can bend. The spine varies in shape and size according to the shapes of the people's bodies. The healthy spine has front-to-back curves. Problems occur when the curvature becomes too large.
It is normal for the spine to curve from front to back but not sideways much. Such a side-to-side curve is called scoliosis. The scoliotic spine is traumatic rotated, twisted and resembles the stripes on a 'barber pole'.
The consequence of a twisted spine is often a rise one side of the chest than the other and the shape of the breastbone changes. One shoulder is higher than the other and clothes tend to hang unevenly as one hip is higher than the other. Scoliosis is different in different people as the combinations of curvatures vary.
Such abnormal spine curves can be due to different causes. While some babies are born with spinal defects called congenital scoliosis, some children suffer muscle diseases, injuries and other illnesses such as cerebral palsy that can cause spinal deformities.
Scoliosis treatment
Treatment options for scoliosis are determined after taking several factors into consideration. The spinal maturity, location, degree and severity of curvature, and the potential for progression are some of the determining factors.
Observation: This is appropriate for small curves where the progression involves low risk. Statistically it has been found that curves with low risk of progression are unlikely to cause problems in adulthood if boys have attained 17 and girls 15 years of age. However, a follow up x-ray once a year is advised to confirm that the curve is not progressing after completion of growth.
Surgery: Surgery for spinal deformity has different approaches. It could be the traditional posterior approach, an anterior one or both. While in posterior approach the surgeon performs the surgery through the patient's back while the patient lies on the stomach, in anterior approach, the surgeon corrects the spinal deformity from the front of the spine. Majority of operations are done using posterior approach, whereas an anterior approach is adopted for certain other types of curvatures such as thoracolumbar spine.
In some cases, a surgeon can recommend a 'front and back' or anterior-posterior spinal surgery. These are adopted when the curves are very severe, stiff and when other attempts at fusion have failed.
A bone graft is done to bridge the gaps which the new bone needs to form in order for the fusion to occur. Bone grafts utilize some form of autogenous bone graft which is taken from the patient's body. The bone comes from the patient's spine, ribs or pelvis. When chips of the bone are removed from certain parts of the spine and then packed in the areas where the fusion is going to occur, this is called local bone grafting.
When a curve occurs in the thoracic vertebrae, a 'rib hump' also occurs. Now the rib cages would appear at different heights. Such a rib hump is corrected to some extent by spinal surgery. A thoracoplasty is performed if the rib deformity remains even after surgery.
Braces for scoliosis
The only non-surgical treatment especially for idiopathic scoliosis is 'bracing'. The aim of bracing is to prevent the curve from progressing as the child grows. Bracing is often effective in stopping the progression of the majority of adolescent scoliotic curves.
A physician would recommend a particular brace and bracing schedule based on several factors such as location of the curve in the child, and degree and severity of curvature.
Success of the bracing treatment depends upon compliance with wearing the back brace as prescribed. However, there could be instances when the spinal curves that are aggressive continue to progress despite bracing. A spinal fusion surgery is recommended. Here again, a back brace can still be beneficial by helping delay in progression of the curvature and allowing the infant to grow more before having a spinal fusion.
- The Thoraco-Lumbo-Sacral-Orthosis-TLSO is called the 'Boston brace' and it is the most common form. It is also referred to as an 'underarm brace.' This brace comes in custom-molded from plastic and it works by applying three-point pressure to the curvature to prevent its progression. The TLSO braces can be worn 23 hours a day and can be taken off to swim, play sports and participate during gym class.
- The Cervico-Thoraco-Lumbo-Sacral-Orthosis, known as a Milwaukee brace, is similar to TLSO brace but includes a neck ring that is held in place by vertical bars attached to the body of the brace. This type of brace is prescribed for thoracic spine and it can be worn for almost 23 hours a day.
- The Charleston Bending Brace called a 'night time brace', as the name indicates is only worn while sleeping. This brace is molded to the patient while they are bent to the side. More pressure is thus applied that bends the child against the curve. The child can go to school and participate in sports normally without anybody else knowing and the negative stigma is avoided here. This
brace is as effective as the other two braces described above. But the curves must be in the 20-40 degrees range and the apex of the curve must be below the level of the shoulder blade for Charleston Bending brace to be effective.
Yoga for scoliosis
Yoga aims to strengthen and cure the scoliosis affected spine through a slow healing process. There is normal tendency for the muscles to become weak due to the asymmetrical posture of scoliosis. Yoga, which is a form of disciplined exercise, can help to certain extent to attain required results. Yoga increases concentration and enables proper circulation to all the compressed areas of the body. Yoga also strengthens the abdomen and legs and prevents lateral curves.
The practice of 'hatha yoga' which involves breathing techniques and relaxation provides benefits such as improved posture and increased flexibility and strength.
Yoga postures and breathing awareness can combine to develop structural alignment and creation of better symmetrical alignment. Through yoga one can find a balance point allowing the scoliosis curve to coexist with gravity and activate the body's natural plumb line.
Yoga promises better posture and less pain for those suffering from scoliosis. And psychologically, doing yoga makes the person feel empowered and there is thus hope yet to improve the condition and quality of living.
Top of the Page: Scoliosis Treatment
Tags:#scoliosis #braces for scoliosis #thoracic scoliosis #idiopathic scoliosis #congenital scoliosis #scoliosis treatment #spine scoliosis #mild scoliosis #yoga for scoliosis
 Slipped Disc
Slipped Disc Knee Replacement for Women
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Osteoarthritis
Drop Wrist Deformity
Ankylosing Spondylitis
Spinal Decompression
Scoliosis Treatment
Cause of Osteoporosis
Osteopenia
Bone Density Test
Disc Herniation
Tennis Elbow Symptoms
Restless Leg Syndrome Symptoms
Other health topics in TargetWoman Women Health section:
General Women Health

Women Health Tips - Women Health - key to understanding your health ...
Cardiac Care
Women's Heart Attack Symptoms - Identify heart problems...
Skin Diseases
Stress Hives - Red itchy spots ...
Women Disorders
Endocrine Disorder - Play a key role in overall wellbeing ...
Women's Reproductive Health
Testosterone Cream for Women - Hormone replacement option ...
Pregnancy
Pregnancy - Regulate your lifestyle to accommodate the needs of pregnancy ...
Head and Face
Sinus Infection - Nearly 1 of every 7 Americans suffer from ....
Women and Bone Care

Slipped Disc - Prevent injury, reduce pain ...
Menstrual Disorders
Enlarged Uterus - Uterus larger than normal size ...
Female Urinary Problems
Bladder Problems in Women - Treatable and curable ...
Gastrointestinal Disorders
Causes of Stomach Ulcers - Burning feeling in the gut ...
Respiratory Disorders
Lung function Test - How well do you breathe ...
Sleep Management

Insomnia and Weight Gain - Sleep it off ...
Psychological Disorders in Women
Mood swings and women - Not going crazy ...
Supplements for Women
Women's Vitamins - Wellness needs...
Natural Remedies

Natural Diuretic - Flush out toxins ...
Alternative Therapy
Acupuncture Point - Feel the pins and needles ...
Women Health Directory
Top of the Page: Scoliosis Treatment
Popularity Index: 101,002

