Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome
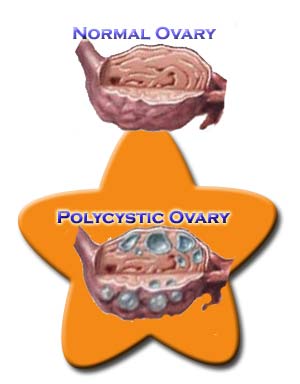
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome or Polycystic Ovarian Disease is a condition that occurs due to an endocrine imbalance. Nearly 5 - 10 % of women of reproductive age suffer from this condition but are sometimes unaware of it. As the name suggests, Polycystic ovarian syndrome is characterized by multiple follicles in the ovaries.
There are multiple cysts in the enlarged ovaries and the follicles are in different stages of maturation. Women suffering from Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) experience infertility due to irregular menstruation or absence of menses. Obesity, unwanted hair growth, diabetes and hypertension are other symptoms of this endocrine disorder.
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) was originally reported by Stein and Leventhal in 1935 when they studied a group of women suffering from amenorrhea (absence of menses), infertility, enlarged polycystic ovaries and hirsutism. Most women who suffer from this condition experience infrequent or irregular menstrual cycles.
In PCOS, under-developed follicles accumulate in the ovaries. Since they fail to mature, they accumulate as cysts in the ovaries. The low levels of follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and elevated levels of androgens may be the reasons for this condition. When there is no ovulation, the progesterone hormone is not created and the lining of the uterus is not shed in a timely fashion. This increases the chances of endometrial hyperplasia and even cancer.
Another feature associated with PCOS is hyper androgenism or increased responsiveness to testosterone. This usually shows up in oily skin and acne. Excess hair may be noticed on the face and other parts of the body. Women suffering from PCOS have a weight problem, especially around the waist. Insulin resistance is also noticed in some women. This increases the risk of developing diabetes in later years.
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome Symptom
- Absence of menses or abnormal or scanty menstrual periods
- Weight gain
- Infertility
- Aggravated acne
- Increased hair growth in a male pattern
- Virilization - a condition where male sex characteristics
High levels of insulin can result in Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome symptoms such as high androgen levels, infertility and lack of ovulation. These symptoms are usually noticed when women are in their 20s or 30s. Diagnosis of PCOS is after a physical examination and laboratory tests. Thyroid and prolactin levels in the blood are tested. Serum levels of male hormones (DHEA and testosterone) are tested for higher than normal levels. Tumors in the ovary or adrenal glands can be diagnosed with vaginal and abdominal ultrasounds. Insulin resistance is vital in the diagnosis of PCOS. Insulin is instrumental in regulating the ovarian function. An ovarian biopsy may also be done.
Treatment for Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome
Treatment for women with Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome depends on what stage of a woman's life this condition has manifested and her fertility desires. Birth control pills are prescribed to regularize the menstrual cycle and reduce the risk of uterine cancer. Other medications used in the treatment of PCOS are flutamide and spironolactone.
Clomiphene induces the pituitary gland to secrete more FSH and this stimulates release and maturity of ova. Insulin resistance is reduced with drugs such as Metformin (Glucophage) and Troglitazone. 'Ovarian drilling' is a process of using laser to place small holes in the ovaries so as to normalize the hormonal environment and allow normal ovulation.
Diet Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome
Since women suffering from polycystic ovarian syndrome face problems of obesity, a healthy diet is vital for the improvement of all symptoms of PCOS. Refined carbohydrates and sugars must be avoided from the diet. Hydrogenated vegetable oils and fried foods must also be avoided in the diet.
Including some nutritional supplements in the form of Zinc and Vitamin A in the diet can help alleviate some of the symptoms of PCOS. Essential Fatty Acids (EFAs) and Panthothenic Acid have shown considerable improvement in the treatment of acne and other symptoms of PCOS. A healthy diet combined with physical activity goes a long way in managing PCOS. A healthy body weight helps in restoring normalcy in the insulin activity.
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome and Pregnancy
Generally higher rates of miscarriage and pregnancy induced elevated blood pressure and diabetes has been associated with pregnant women suffering form polycystic ovarian syndrome. But the drug Metformin has helped women by reducing male hormone levels and limiting weight gain. Clomiphene Citrate tablets are used to induce ovulation. Sometimes gonodotropin injections are also used to stimulate ovulation and aid pregnancy in women with polycystic ovarian syndrome.
Top of the Page: Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome
Tags:#polycystic ovarian syndrome #polycystic ovarian syndrome symptom #treatment for polycystic ovarian syndrome #diet polycystic ovarian syndrome #polycystic ovarian syndrome and pregnancy

Enlarged Uterus
Bacterial Vaginosis
Yeast Infection
Irregular Menstrual Cycle
PMS - Menstruation
Dysmenorrhea
Hypomenorrhea
Mid Cycle Bleeding
Pelvic Organ Prolapse
Vaginal Atrophy
Cervix Cancer
Abnormal Pap Smear
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome
Ovulation Pain
Uterine Prolapse
Fibroid Tumor
Menorrhagia
Endometriosis Symptom
Galactorrhea
Hysterectomy
Blocked Fallopian Tubes
Menopause and Weight Gain
Premature Menopause
Surgical Menopause
Other health topics in TargetWoman Women Health section:
General Women Health

Women Health Tips - Women Health - key to understanding your health ...
Cardiac Care
Women's Heart Attack Symptoms - Identify heart problems...
Skin Diseases
Stress Hives - Red itchy spots ...
Women Disorders
Endocrine Disorder - Play a key role in overall wellbeing ...
Women's Reproductive Health
Testosterone Cream for Women - Hormone replacement option ...
Pregnancy
Pregnancy - Regulate your lifestyle to accommodate the needs of pregnancy ...
Head and Face
Sinus Infection - Nearly 1 of every 7 Americans suffer from ....
Women and Bone Care

Slipped Disc - Prevent injury, reduce pain ...
Menstrual Disorders
Enlarged Uterus - Uterus larger than normal size ...
Female Urinary Problems
Bladder Problems in Women - Treatable and curable ...
Gastrointestinal Disorders
Causes of Stomach Ulcers - Burning feeling in the gut ...
Respiratory Disorders
Lung function Test - How well do you breathe ...
Sleep Management

Insomnia and Weight Gain - Sleep it off ...
Psychological Disorders in Women
Mood swings and women - Not going crazy ...
Supplements for Women
Women's Vitamins - Wellness needs...
Natural Remedies

Natural Diuretic - Flush out toxins ...
Alternative Therapy
Acupuncture Point - Feel the pins and needles ...
Top of the Page: Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome
Popularity Index: 100,928

