Lyme Disease
Lyme borreliosis or Lyme disease is an infectious disease caused by the bite of an infected tick. Infected ticks carry a bacterium called spirochete. Infected ticks spread these bacteria by biting animals and humans. Not all people who have had tick bites develop Lyme disease; only people bitten by infected ticks develop the disease.
Tick bites might go unnoticed in a few; these people might not realize the onset of the disease symptoms. Many people who develop Lyme disease do not remember being bitten by ticks. Therefore it is important to know and watch for symptoms of Lyme disease.
Ticks are small and can be hardly seen. Immature ticks or nymphs are as big as a poppy seed. Adult ticks resemble the size of a sesame seed. Ticks have to be removed the moment you see them. This might prevent Lyme disease. Lyme disease is spread by infected ticks only if they have been attached to the body for at least 36 hours. The disease is named after the town of Lyme, Connecticut, USA. Lyme disease is common in the United States, Canada, Europe, and Asia.
May through August (during spring and summer) is the riskiest period for the spread of Lyme disease. The ticks are very active during this period as people spend more time outdoors. Lyme disease is not contagious and will not spread through touch but a person suffering from Lyme disease should not donate blood to another healthy person.
Lyme disease causes
Bacteria present in ticks cause Lyme disease. Two types of ticks are identified as major causes for spreading Lyme disease bacteria
Western black-legged ticks: present along the pacific coast
Deer ticks: present in the northeast and Midwest parts of USA
Lyme disease symptoms
Early stages
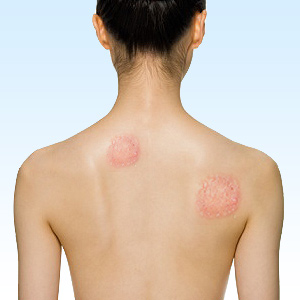
- Circular rashes show up within 1-2 weeks of infection. This is the first sign of infection. A few people might not develop any rash at all.
- The rash usually resembles a bull's-eye and has a central red spot surrounded by clear skin.
- The rash may be warm to touch but is not painful or itchy.
- In people with darker skin tones, it is difficult to see the rash.The rash usually resolves in about a month.
- Along with the rash, a person might have flu-like symptoms such as swollen lymph nodes, fatigue, headache, and muscle aches.
In a few people the symptoms settle down without treatment, but in a few more the infection tends to spread to other parts of the body.
- Infection spreads to other parts of the body.
- Symptoms for the second stage of Lyme disease usually appear within several weeks after the tick bite.
- These symptoms might show in people who had not developed the initial rash.
- Tiredness is the most often reported symptom.
Third or final stage symptoms
If left unattended during the initial stages, Lyme disease can cause symptoms like:
- Chest pain and affect the heart
- Affects nervous system thus leading to Bell's palsy
- Tingling and numbness in the legs and arms
- Stiff neck
- Headaches
- Swelling and pain of the large joints
The above mentioned symptoms can show up within few weeks from the onset of Lyme disease. If left untreated, it might cause symptoms like:
- Swelling and joint pain (like arthritis)
- Tingling and numbness in hands, feet, and back
- Weakness or paralysis of face muscles
- Lack of energy
- Trouble focusing on thoughts
- Poor memory
Lyme disease diagnosis
The doctor will begin with a physical examination. Questions like:
- When the rashes started off?
- How long has it been there?
- When did you notice it first?
- What were your activities before the rashes set in?
The doctor might also order for blood tests. Blood tests (IgM and IgG) can detect antibodies for Lyme disease only after a few weeks after being infected. Antibody tests are conducted on fluid from joint or spine. If these tests are inconclusive, ELISA test is done to screen for Lyme disease. The Western Blot test confirms the results and can detect chronic Lyme disease infection.
Lyme disease treatment
Lyme disease can be cured with antibiotics. Antibiotics can cure the condition within 3 weeks of starting the treatment. The moment you notice abnormal rashes, it is suggested you visit your doctor. Treatment for Lyme disease should be started immediately. If you have had a tick attached to your skin, talk to your doctor immediately especially if you live in an area where Lyme disease has been reported.
There is no home treatment for Lyme disease as the conditions will settle down only after taking antibiotics. Hence it is advisable to check with your physician before you begin medications.
Preventing Lyme disease
- Protecting yourself from ticks is the best way to prevent Lyme disease.
- When you go to wooded or grassy areas, cover up as much skin as you can.
- Use a bug spray to repel ticks.
- Though you can't get Lyme disease from your pet, they can bring infected ticks indoors. So it is advisable to check your pets for ticks after they've been outside.
- Wear a long-sleeved shirt, hat, long pants and remember to tuck your legs into the socks.
There is no vaccination to prevent Lyme disease.
Found a tick on your body?
- Do not panic.
- Use a pair of fine-tipped tweezers to hold the tick.
- Pull the tick in the upward direction, away from your body.
- Do not squeeze or twist the tick while pulling it out.
- If any part of the tick remains in your body, pull it out as you pull out a small particle.
- Apply an antiseptic.
- Wash your hands thoroughly.
- If you develop rashes, meet up with your doctor.
- If you are bitten by a tick and you develop no rashes or any other symptom, you need not take antibiotics.
Top of the Page: Lyme Disease
Tags:#Lyme disease #Lyme disease symptoms #Lyme disease treatment

Endocrine Disorder
Thyroid Disorder
Adrenal Fatigue Syndrome
Generalized Anxiety Disorder
Panic Disorder
Borderline Personality Disorder Women
Binge Eating Disorder
Dysthymic Disorder
Chronic Fatigue Syndrome
Lyme Disease
Diet and Kidney Disease
Anorexia Nervosa
Sarcoidosis Disease
Other health topics in TargetWoman Women Health section:
General Women Health

Women Health Tips - Women Health - key to understanding your health ...
Cardiac Care
Women's Heart Attack Symptoms - Identify heart problems...
Skin Diseases
Stress Hives - Red itchy spots ...
Women Disorders
Endocrine Disorder - Play a key role in overall wellbeing ...
Women's Reproductive Health
Testosterone Cream for Women - Hormone replacement option ...
Pregnancy
Pregnancy - Regulate your lifestyle to accommodate the needs of pregnancy ...
Head and Face
Sinus Infection - Nearly 1 of every 7 Americans suffer from ....
Women and Bone Care

Slipped Disc - Prevent injury, reduce pain ...
Menstrual Disorders
Enlarged Uterus - Uterus larger than normal size ...
Female Urinary Problems
Bladder Problems in Women - Treatable and curable ...
Gastrointestinal Disorders
Causes of Stomach Ulcers - Burning feeling in the gut ...
Respiratory Disorders
Lung function Test - How well do you breathe ...
Sleep Management

Insomnia and Weight Gain - Sleep it off ...
Psychological Disorders in Women
Mood swings and women - Not going crazy ...
Supplements for Women
Women's Vitamins - Wellness needs...
Natural Remedies

Natural Diuretic - Flush out toxins ...
Alternative Therapy
Acupuncture Point - Feel the pins and needles ...
Top of the Page: Lyme Disease
Popularity Index: 101,046

